How to Successfully Order Custom Castings: A Step-by-Step Guide
Metal casting has shaped human civilization since 4000 BC , evolving from ancient bronze statues to today's precision-engineered components. In the modern world, this transformative process—where molten metal is poured into carefully designed molds—drives a global industry worth over Us$179.08 billion.
Custom castings represent the cutting edge of this field, where advanced engineering meets ancient craft to create components that precisely match specific requirements.
The impact of custom castings touches virtually every aspect of modern life. From the engine blocks powering your car to the massive turbine housings generating electricity, from delicate medical devices to robust mining equipment, custom castings provide the backbone for countless industries. Their applications span an impressive range:
- Automotive components requiring exceptional durability
- Precision aerospace parts where failure isn't an option
- Heavy machinery for construction and farming
- Intricate architectural elements in landmark buildings
- Critical components in renewable energy systems
- Custom parts for shipbuilding and rail transportation
- Specialized equipment for oil and gas extraction
- Robust processing equipment for forestry and mining
While the possibilities are nearly limitless, achieving success in custom casting requires meticulous attention to detail and comprehensive planning. From initial design concepts to final production, each step demands careful consideration to ensure the finished product meets exact specifications while remaining cost-effective. This guide by Align Manufacturing will walk you through every crucial aspect of ordering custom castings, helping you navigate the complexities of this sophisticated manufacturing process.

1.Design Specifications
The first step in ordering custom castings is defining the design requirements. This includes:
Component Requirements
- The component's function
- Shape and dimensions
- Required mechanical properties
- Quantity needed
Critical Design Elements
- Minimum Section Thickness: Typically no thinner than 0.25 in (6 mm) for conventional processes
- Draft Requirements: Generally 3/16 in of draft per ft (approximately 1.5 degrees)
- Parting Line Considerations: Straight parting lines reduce costs and simplify production
- Core Design: Consider accessibility for core removal and minimum diameter requirements.
Mold Preparation: Crafting the Cavity
Core Design Considerations
The minimum diameter of a core depends on:
- The thickness of surrounding metal
- Core length
- Special foundry procedures
- Reinforcement needs for larger cores
- Accessibility for core removal
Collaborating with a casting manufacturer early ensures the design aligns with both functional requirements and manufacturability. Utilizing 3D modeling and simulations helps visualize the final product and identify potential design challenges.
2. Material Selection
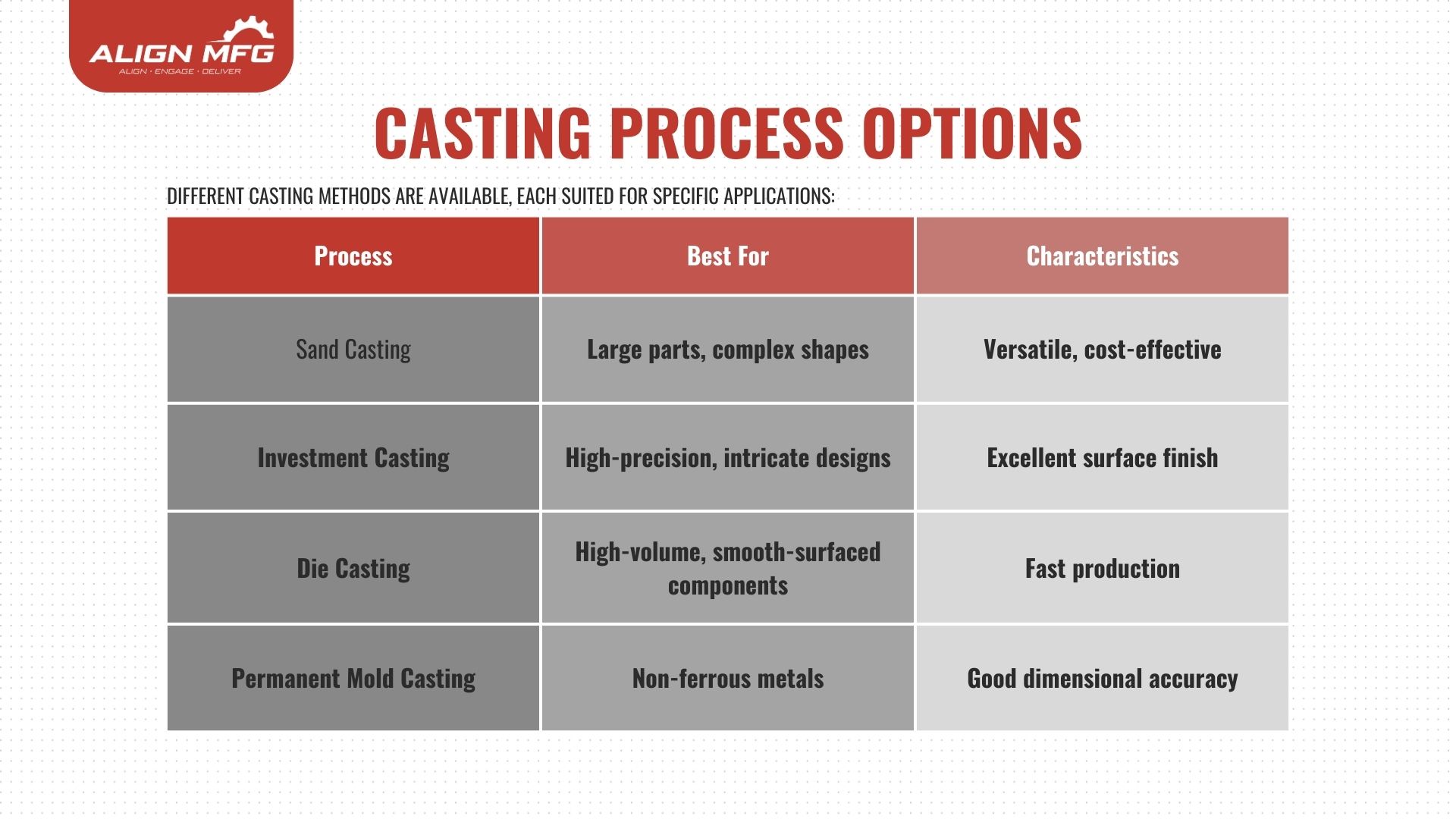
Selecting the right material is crucial as it impacts performance, durability, and cost. Common casting materials include:
- Steel: High strength and wear resistance
- Aluminum: Lightweight with good corrosion resistance
- Brass/Bronze: Excellent for corrosion-resistant applications
- Specialized Alloys: Used for extreme environments
Material Selection Factors
- Required strength and hardness
- Corrosion and heat resistance
- Machinability and finishing needs
- Industry-specific regulations (e.g., ASTM, ISO)
4. Soundness & Quality Considerations
Understanding that perfect castings are impossible is crucial. Quality considerations include:
Defect Types
- Sand inclusions
- Slag inclusions
- Macroporosity
- Shrinkage
The Importance of Quality Control in Custom Casting Production
Establishing rigorous quality control (QC) measures is crucial to ensuring that custom castings meet performance requirements, comply with industry standards, and minimize costly defects. A well-defined QC process helps align manufacturing with customer expectations, ensuring consistent production and preventing disputes over acceptance criteria.
Key Quality Control Measures for Custom Castings
To maintain high standards, foundries and customers must establish clear acceptance and rejection criteria before production begins. Essential QC factors include:
✔ Acceptance & Rejection Criteria
- Clearly define the allowable defect levels and ensure both parties agree on what constitutes acceptable variations.
- Use recognized international standards (such as ASTM, ISO, or SAE) to benchmark quality expectations.
✔ Dimensional Tolerances & Surface Finish Requirements
- Specify critical tolerances to ensure precision and fit for the intended application.
- Define surface finish expectations based on the casting process used (e.g., investment casting vs. sand casting).
- Consider post-processing treatments (such as grinding, polishing, or machining) to achieve the required finish.
✔ Defining the Exact Alloy Specification
- Specify the exact metal alloy to be used, referencing an internationally recognized standard (ASTM, ISO, EN, or JIS).
- Different alloys offer varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
- Ferrous Metals (Iron-Based): Cast steel (most common), stainless steel, ductile iron, malleable iron.
- Non-Ferrous Metals (Non-Iron-Based): Aluminum, copper, and specialty alloys.
✔ Soundness & Defect Control in Castings
- No casting is 100% free of defects, but strict control over metal purity, shrinkage, and porosity helps minimize imperfections.
- Implement Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) such as:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Detects internal flaws.
- Radiographic Testing (X-ray): Examines internal structures for porosity and inclusions.
- Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT): Identifies cracks and surface defects.
- Foundries must follow ASTM acceptance criteria for evaluating defects and determining whether a casting meets specifications.
✔ Heat Treatment & Mechanical Properties
- Mechanical properties (strength, hardness, ductility, etc.) depend on solidification conditions, cooling rates, and heat treatment processes.
- Some alloys require post-casting heat treatment to achieve specific mechanical properties.
- Heat treatment options include:
- Normalizing & Annealing: Enhances ductility and removes internal stresses.
- Flame Hardening & Case Hardening: Improves surface hardness for wear resistance.
- Tempering & Quenching: Adjusts strength and toughness to required specifications.
Align Manufacturing ensures precise temperature control and monitoring using advanced heat treatment equipment to maintain consistent quality across production batches.
5. Prototyping
Before full-scale production, creating prototypes allows for functional testing through:
- 3D Printing
- Small-Batch Casting
- CNC Machining
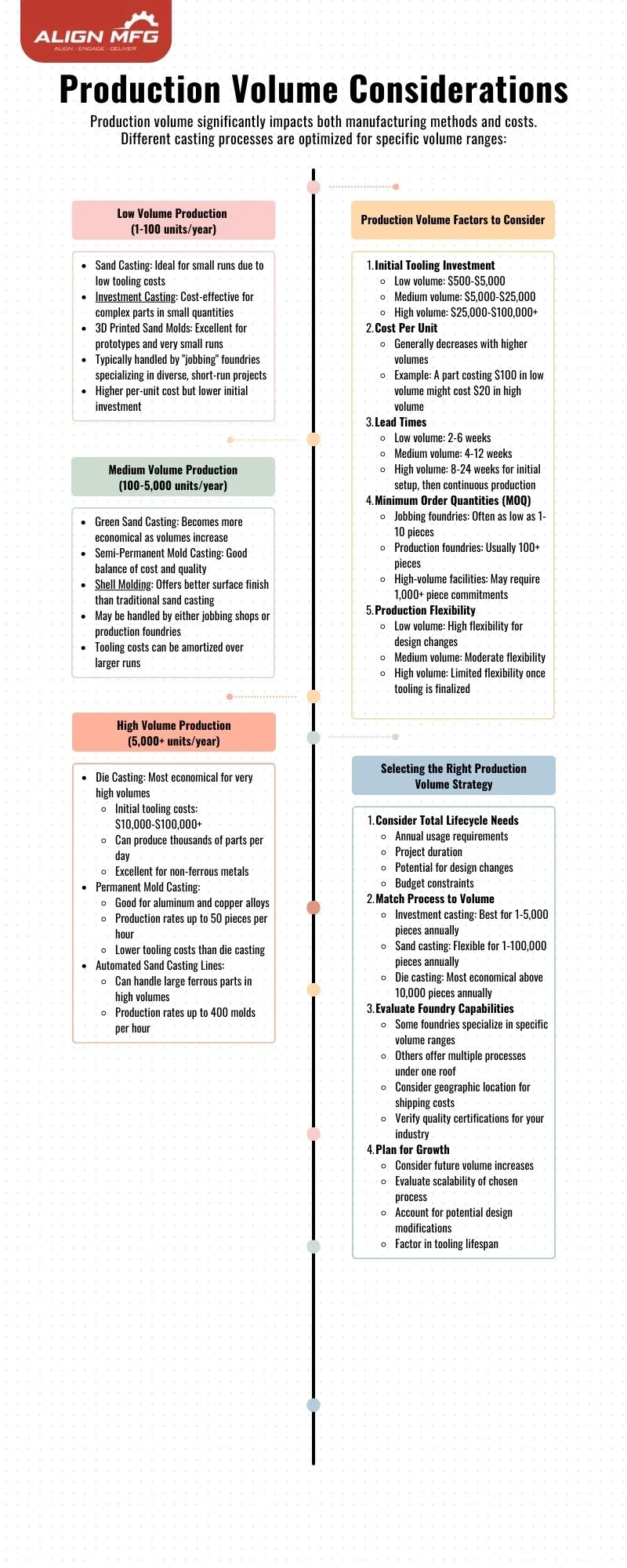
6. Weight Considerations
Weight impacts both cost and production methods:
Weight Factors
- Net Weight: Final casting weight
- Gross Weight: Total metal poured, including gates and risers
- Casting Yield: Efficiency ratio between net and gross weight
- Material Cost Impact: Higher weight increases material costs
Let me streamline this into the most practical calculation that foundries commonly use.
Weight and Yield Calculations in Casting
The most critical calculation in casting is determining the total material needed and its cost, as this directly impacts project feasibility and pricing.
Key Weight Components
- Net Weight (Wn): Final casting weight
- Gross Weight (Wg): Total metal poured (including feeding system)
- Casting Yield: Efficiency ratio (typically 60-75% for sand casting)
Essential Casting Calculation Example
Let's say you need to produce a steel casting weighing 100 kg (net weight):
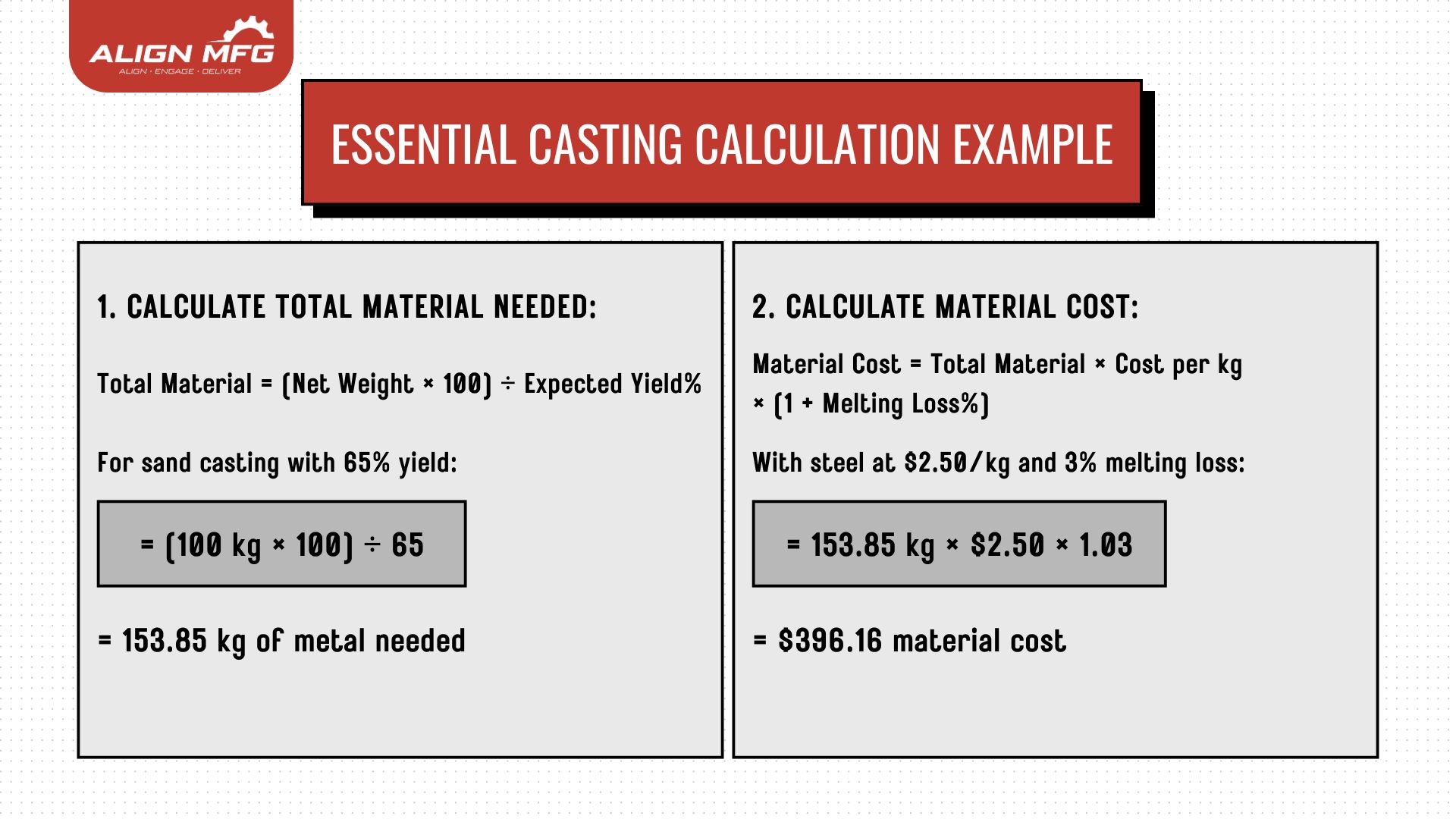
This basic calculation helps:
- Determine material requirements
- Estimate project costs
- Set appropriate pricing
- Plan production efficiency
Typical Yield Ranges (for reference):
- Sand Casting: 60-75%
- Die Casting: 85-95%
- Investment Casting: 55-65%
7. Pattern Equipment & Tooling
Pattern quality directly affects casting quality and costs:
Types of Patterns
Each pattern type offers distinct advantages and trade-offs:
- Wood Patterns
- Pros: Lower initial cost, easier to modify
- Cons: Shorter lifespan, can warp over time
- Best For: Low-volume production, prototyping, and sand casting
- Metal Patterns
- Pros: High durability, maintains precision over many cycles
- Cons: Higher upfront cost, heavier, harder to modify
- Best For: High-volume production, die casting, investment casting
- Mounted vs. Loose Patterns
- Mounted: Affixed to a plate for consistent alignment, improving repeatability
- Loose: Freely placed in the mold, more flexible but can lead to variations
- Split Patterns
- Used to simplify mold separation and improve accuracy in complex geometries
- Can involve full split core boxes or half core boxes, depending on foundry requirements

Pattern Considerations & Cost Implications
The decision on pattern design must take into account long-term costs, foundry compatibility, and quality control. Some key considerations include:
- Compatibility with Foundry Equipment
- Even if an existing pattern is available, a foundry may require new tooling to match its specific machinery.
- This can involve:
- Full split core boxes instead of half core boxes
- Metal pattern replacement for wooden patterns
- Switching to mounted patterns for better consistency
- Balancing Upfront Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
- More sophisticated pattern equipment leads to higher pattern costs initially.
- However, this investment reduces per-unit casting costs over time by:
- Increasing efficiency
- Improving dimensional accuracy
- Reducing scrap and rework
- Example: A metal pattern may cost 2-3x more than a wooden one, but for large-scale production, it can lower overall casting costs due to reduced wear and fewer defects.
- Storage & Maintenance
- Patterns require proper storage and maintenance to prolong their usability.
- Foundries may charge for pattern storage or request maintenance fees, especially for high-volume production.
- Investing in high-quality pattern materials reduces maintenance frequency and improves overall casting consistency.
The Design Phase: Pattern Creation
8. Testing & Inspection
Comprehensive testing ensures quality through:
Destructive Testing
- Requires separate test castings
- Provides internal soundness verification
- Used to validate production methods
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
- Visual Inspection
- Liquid Dye Penetrant Inspection (LPI)
- Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI)
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
- Radiographic Inspection (X-Ray)
9. Machining Requirements
Machining considerations affect both design and cost:
Machining Factors
- Stock allowance for machined surfaces
- Fixture and clamping requirements
- Material specification impacts
- Production quantity considerations
Verification Process
- Complete layout for complex machining
- Target point marking
- First article inspection
- Machining allowance verification
10. Supplier Selection
Choose a reliable foundry based on:
- Experience & Expertise
- Certifications
- Production Capabilities
- Quality Control Measures
- Specialization (short-run vs. high-volume)
11. Requesting a Quote
Provide detailed information including:
- Technical Drawings
- Material Specifications
- Production Quantity
- Finishing Requirements
- Testing Requirements
- Delivery Timeline
12. Production & Delivery Timelines
Understanding typical timelines is crucial:
Timeline Components (up to 24 weeks)
- Commercial Administration
- Pattern/Tooling Construction
- Sampling
- Inspections
- Pattern Modifications
- Production Setup
- Manufacturing
- Post-Production Processing
Production Planning
- Early communication of delivery requirements
- Regular progress updates
- Buffer time for unexpected issues
- Quality control checkpoints
Final Thoughts
Success in custom casting projects requires:
- Thorough planning and design
- Clear communication with suppliers
- Understanding of manufacturing constraints
- Comprehensive quality control
- Realistic timeline expectations
By considering all these factors during the planning and ordering process, you can achieve cost-effective and high-performance custom castings suited to your needs.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
For more information or to discuss your specific project needs, contact us today.