What is Gravity Die Casting?
Gravity die casting is a metal casting technique that uses gravity rather than external pressure to fill a mold. In this process, molten aluminum is poured into a steel or iron mold, known as a "die," where it flows down into the mold cavity under the force of gravity. This method differs from other types of casting, such as high-pressure die casting, as it relies solely on the natural pull of gravity, resulting in less turbulent flow and fewer air pockets. The result is a dense, high-quality metal part with excellent dimensional accuracy and strength, making it especially suitable for components requiring durability and precision.
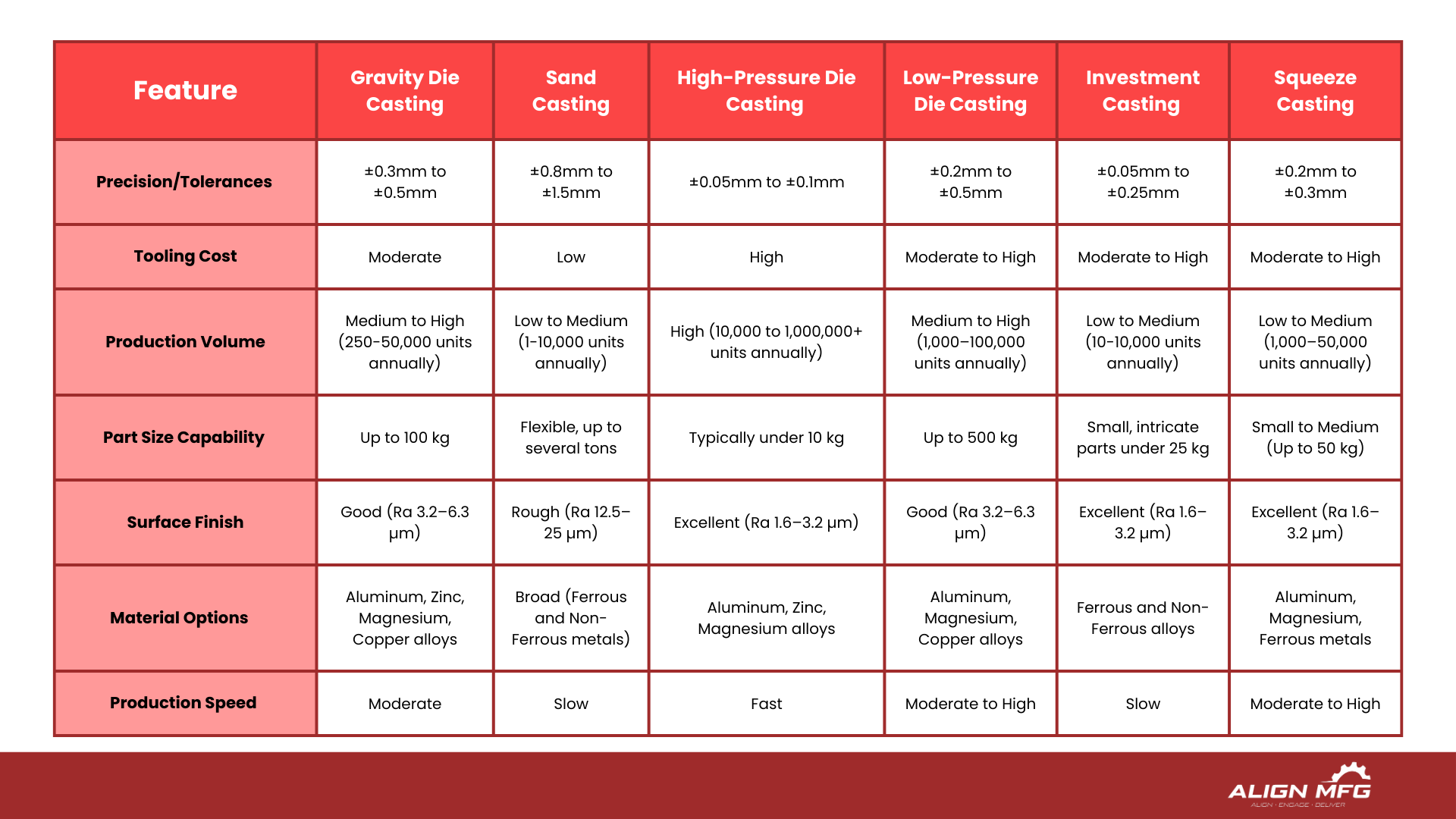
The process achieves tolerances of ±0.3mm to ±0.5mm, with wall thickness capabilities ranging from 3mm to 20mm. Parts can range from small components weighing 0.1 kg to larger pieces up to 100 kg, offering remarkable versatility in production capabilities.
Compared to sand casting, gravity die casting is more efficient in terms of both material use and production time. The reusable steel or iron molds used in gravity casting allow for rapid production cycles and consistent quality across batches, making it a cost-effective solution for medium-to-high volume production runs.Its ability to produce parts in quantities ranging from 250 to 50,000 units per annum makes it a popular choice.This adaptability is achieved through its efficient use of resources and streamlined production cycles.
Process of Aluminum Gravity Die Casting
The aluminum gravity die casting process is straightforward yet precise, requiring careful handling and skilled workmanship to ensure optimal results. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the process works:
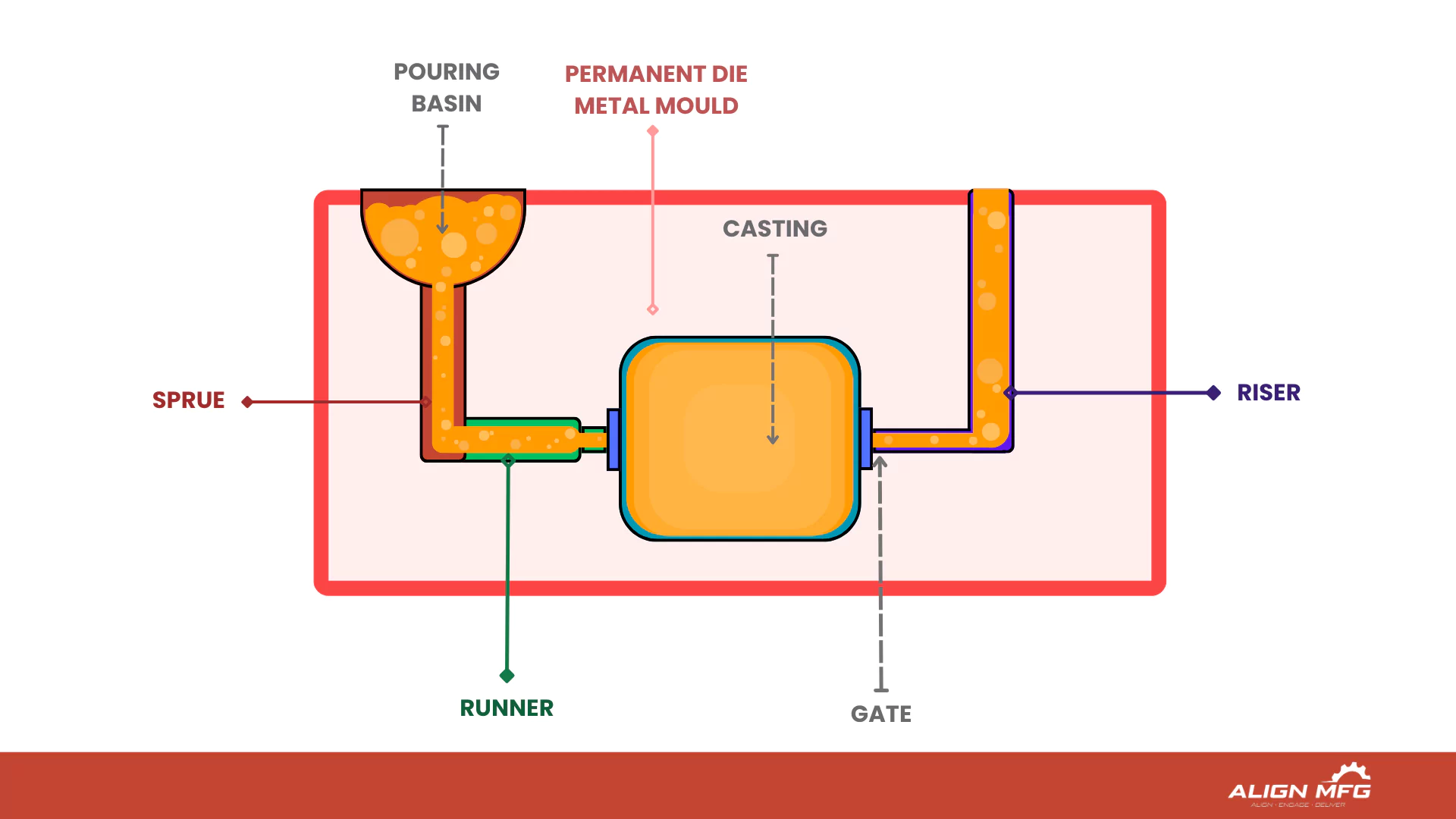
1.Preparing the Mold
The process begins with preheating the die to temperatures between 200-300°C to prevent thermal shock and ensure smooth flow of molten aluminum, which is typically heated to 650-750°C. Lubricants are applied to the mold to help with release after solidification. The mold design incorporates specific features like draft angles of 2-3° for external surfaces and strategically placed parting lines to ensure optimal results."
2.Pouring the Molten Aluminum
Once the mold is ready, molten aluminum is poured into the mold cavity. As gravity pulls the molten metal into every corner of the mold, it begins to fill the cavity, shaping the metal according to the mold’s design. This step requires precise control to ensure an even flow and avoid air pockets.
3.Solidification and Cooling
After pouring, the aluminum is left to solidify within the mold. The cooling phase is crucial, as controlled cooling can impact the material's final properties, such as its strength and structural integrity. Faster cooling generally produces finer grain structures, which can enhance the material's durability.
4.Removing the Casting
Once the metal has solidified and cooled to a manageable temperature, the mold is opened, and the casting is removed. Any residual material, such as sprues or runners, is trimmed off in preparation for the finishing process.
5.Finishing and Inspection
The final casting may go through secondary operations like machining, polishing, or surface treatments to achieve the desired finish and precision. Each part undergoes inspection to ensure it meets quality standards and specifications before moving on to the next phase.
Advantages of Aluminum Gravity Die Casting
Aluminum gravity die casting offers several distinct advantages that make it an attractive choice for various industries. Here are some of the key benefits:
- High Dimensional Accuracy
Gravity die casting produces components with precise dimensions and excellent surface finishes, reducing the need for additional machining. This accuracy is ideal for parts that must meet tight tolerances and specifications.Compared to alumnium sand casting - Superior Strength and Density
Quality control is paramount in gravity die casting. The process includes comprehensive testing methods such as X-ray inspection, pressure testing, and dimensional verification to prevent common defects like porosity and shrinkage. Surface finishing options range from as-cast finish to various post-processing treatments including machining, coating, and painting, depending on the application requirements. - Cost-Effective for Medium-to-High Production Volumes
The reusable nature of steel or iron molds makes gravity die casting cost-effective for medium-to-high production runs. The upfront investment in the mold is offset by the long-term savings from its reusability and the consistency it provides. - Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Components produced by gravity die casting generally exhibit better mechanical properties compared to sand-cast parts, thanks to the controlled cooling and reduced air entrapment. These properties make gravity die-cast parts suitable for applications where durability and longevity are critical. - Eco-Friendly and Less Material Waste
Gravity die casting tends to produce less material waste than sand casting, as the molds can be reused multiple times. The efficiency of the process also reduces the need for excess metal, making it more environmentally friendly. - Improved Production Speed
The rapid cooling time of metal molds in gravity die casting allows for faster production cycles, making it a practical choice for projects needing quick turnarounds without sacrificing quality.
Aluminum Gravity Die Casting Applications
Aluminum gravity die casting is widely used across various industries, especially in sectors where precision, strength, and reliability are paramount. Some of the common applications include:
- Automotive Industry
Gravity die casting is often used to create engine components, transmission cases, and suspension parts. Aluminum alloy A357 is particularly favored for its higher strength properties, while A356 is chosen for parts requiring excellent fluidity and corrosion resistance. The process's ability to maintain uniform wall thickness and proper corner radii makes it ideal for complex automotive components. - Aerospace Industry
Aerospace manufacturers use gravity die casting for parts that require excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Components like housings, brackets, and supports benefit from the dimensional accuracy and structural integrity of gravity-cast aluminum. - Industrial Machinery
Many machinery parts, including hydraulic components, pump housings, and gearboxes, are produced using gravity die casting. Using alloys like A356 for its excellent fluidity and corrosion resistance, these components can be manufactured with wall thicknesses ranging from 3mm to 20mm. The process ensures uniform material properties through controlled cooling and proper mold design, incorporating features like strategic parting lines and adequate draft angles (2-3°) for easy part removal.
- Consumer Electronics and Appliances
Aluminum gravity die casting is also common in consumer electronics and home appliances, where it’s used to create durable, lightweight casings and structural parts. The method’s accuracy and finish quality are ideal for products with aesthetic and functional requirements. - Medical Equipment
Medical devices and equipment that require reliable, corrosion-resistant parts often incorporate gravity die-cast aluminum components. From casings to support structures, gravity die casting ensures that medical equipment meets high standards for both safety and durability. - Marine Industry
Due to aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance and strength, gravity die-cast aluminum parts are widely used in marine applications such as motor housings, brackets, and propeller blades. These components benefit from the durability and resistance to seawater corrosion that gravity casting provides.
Types of components
Gravity Die Casting (GDC), which is typically used for producing medium to high-precision parts with moderate complexity, here are the relevant components that Align Manufacturing could produce using GDC:
1. Oil & Gas Industry Components
- Flanges: High-strength parts used to connect pipes and equipment, benefiting from the precision and consistency of GDC.
- Valve Bodies: Ideal for controlling fluid flow, requiring dimensional accuracy and durability.
- Impellers: Used in pumps for fluid movement, made with fine surface finishes and low porosity offered by GDC.

2. Truck & Trailer Industry Components
- Suspension Parts: Durable components benefiting from GDC's ability to produce parts with high structural integrity.
- Engine Brackets: Precision-engineered to securely mount engines while reducing vibrations.
- Brake Rotors: Made with precise dimensions and excellent surface finishes for consistent braking performance.
- Hubs: Cast with high accuracy to support smooth wheel rotation.

- Industrial Components
- Manhole Covers: High-strength covers that can be precisely cast for consistent performance.
- Vent Release Valves: Suitable for precise control of gases or liquids, taking advantage of GDC’s low porosity properties.
Best Practices and Quality Control
- Mold Design Optimization:
- Proper gating system design for smooth metal flow
- Strategic placement of cooling channels
- Adequate venting to prevent gas entrapment
- Draft angles of 2-3° minimum for external surfaces
- Temperature Management:
- Die preheating to 200-300°C
- Maintaining consistent pouring temperature (650-750°C)
- Controlled cooling rates for optimal material properties
- Quality Assurance:
- X-ray inspection for internal defects
- Pressure testing for leakage
- Dimensional verification using precision measurement tools
- Surface finish inspection and testing
- Surface Finishing Options:
- As-cast finish for non-critical surfaces
- Machining for precise dimensional requirements
- Various coating options for enhanced durability
- Paint preparation and application when required
Conclusion
Aluminum gravity die casting remains a vital process for producing high-quality, precise components across various industries. Its unique combination of strength, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for applications ranging from automotive to medical equipment. By using gravity to guide molten metal into molds, this casting method achieves impressive dimensional accuracy and surface finish, meeting the needs of industries that demand reliability and durability.
If you’re interested in learning more about other casting methods and how they compare, explore the wide range of casting processes available on Align Manufacturing’s website. Each method offers unique benefits tailored to specific applications, helping you find the perfect solution for your manufacturing needs.