In the world of metal manufacturing, choosing the right material for your components can make or break a project.
The materials you select can impact everything from durability to cost-effectiveness. This article will dive deep into the various types of materials commonly used for metal components.
When it comes to manufacturing and industrial applications, metal components are indispensable. These materials are chosen based on specific properties like strength, corrosion resistance, ductility, cost and more. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the characteristics, advantages, and common uses of several metals.
Types of Metals
Aluminum: Lightweight
and Versatile
Stainless Steel: Strength and
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and resistance to corrosion, making it a popular choice in many demanding environments.
Duplex Steel:
A Hybrid Solution
Duplex steel combines the best properties of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, resulting in a material that offers superior performance.
Gray and Ductile Iron:
Versatility and Strength
Iron, in its various forms, remains a cornerstone in manufacturing, particularly gray and ductile iron.
Carbon Steel:
Cost-Effective and Robust
Zinc: Protective
and Functional
Copper: Conductive
and Durable
Copper is highly valued for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability.
Alloys: Customizable
and High-Performance
Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals, engineered to have specific properties not found in pure metals.
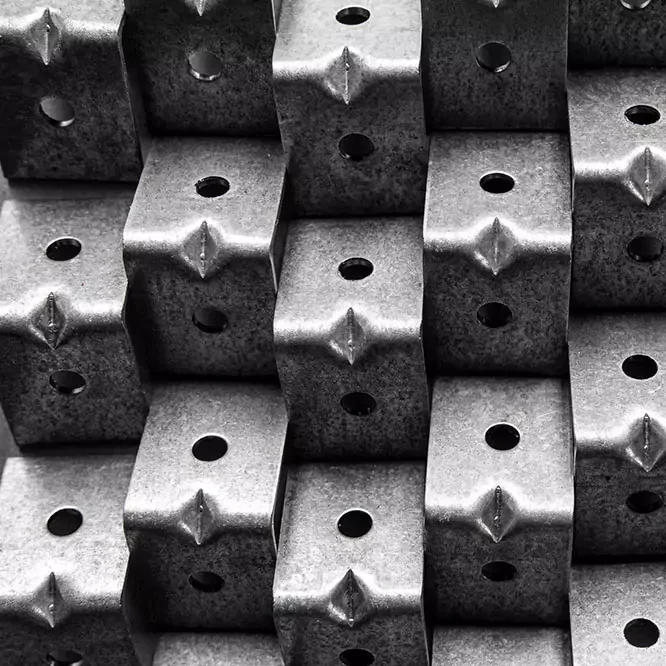
Metal Applications
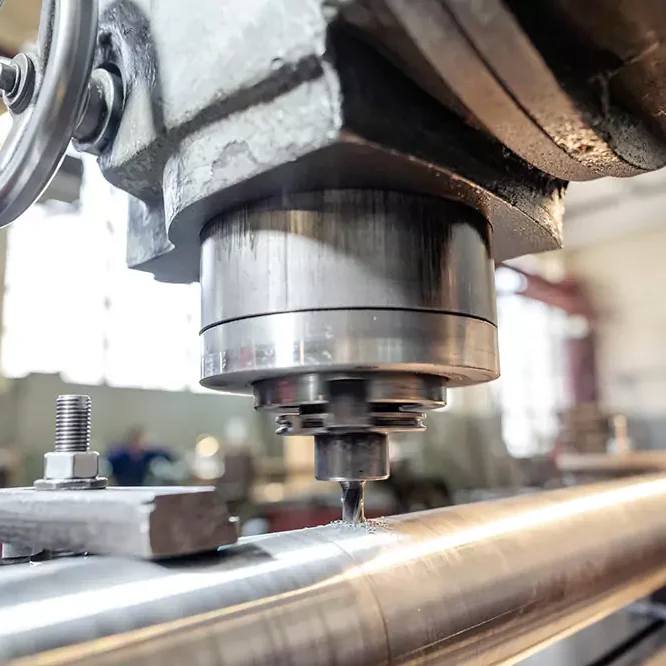
Our Precision-Driven Manufacturing Processes
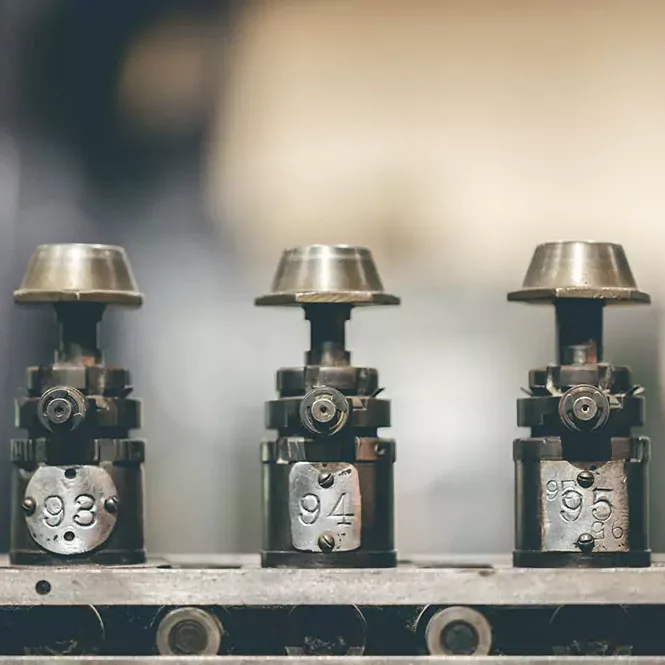
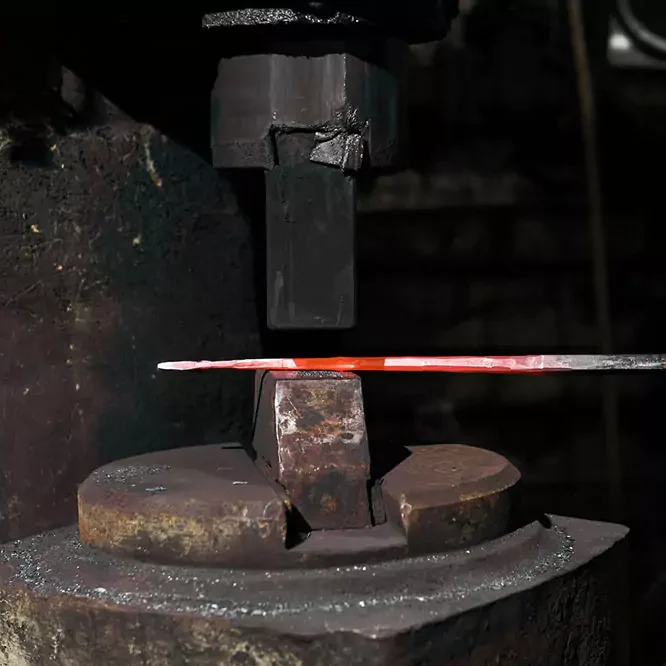
At Align Manufacturing, we excel in the metal production industry, utilizing state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies and highly skilled operators. We transform raw materials into precision-engineered products through a variety of specialized processes. Our expertise encompasses sand casting, investment casting, precision machining, stamping, forging, and fabrication.

Align Manufacturing, we pride ourselves on our commitment to producing quality metal parts. Our experienced team utilizes equipment and processes to ensure each component meets the highest standards of precision and reliability.
We continuously strive to innovate and improve our methods, ensuring that our clients receive parts that not only meet but exceed their expectations in performance and durability. With a focus on excellence and customer satisfaction, Align MFG remains a trusted partner for all your metal needs.
We're dedicated team of local professionals passionately committed to fueling your project's success. Our team is dedicated to maintaining a keen eye for detail in every aspect of the process, from design to delivery. Simultaneously, we prioritize clear, consistent communication with you to ensure that your vision a and requirements are fully understood and met.